Using Google Search Console sets the stage for this enthralling narrative, offering readers a glimpse into a story that is rich in detail with american high school hip style and brimming with originality from the outset.
Google Search Console is a powerful tool that website owners can leverage to enhance their online visibility and performance. From setting up your account to analyzing performance reports, this guide will take you through the ins and outs of maximizing your online presence using Google Search Console.
Overview of Google Search Console

Google Search Console is a free tool provided by Google that helps website owners monitor, maintain, and troubleshoot their website’s presence in Google search results. It offers a variety of features and functionalities to improve a website’s visibility and performance.
Purpose and Benefits, Using Google Search Console
Google Search Console allows website owners to:
- Monitor website performance in Google search results
- Identify and fix indexing issues
- Optimize content for better visibility
- Receive alerts for potential issues affecting the site
- Analyze search traffic data and performance
Main Features and Functionalities
The key features of Google Search Console include:
- Index coverage report to identify indexing issues
- Performance report to analyze search traffic data
- URL inspection tool to check how Google views a specific URL
- Sitemap submission for better crawling and indexing
- Mobile usability report to ensure the site is mobile-friendly
Improving Online Presence
By utilizing Google Search Console, website owners can:
- Optimize content for relevant s
- Fix indexing issues that may hinder visibility
- Monitor search performance and make data-driven decisions
- Ensure the website is mobile-friendly and user-friendly
- Receive important alerts and notifications from Google
Setting up Google Search Console
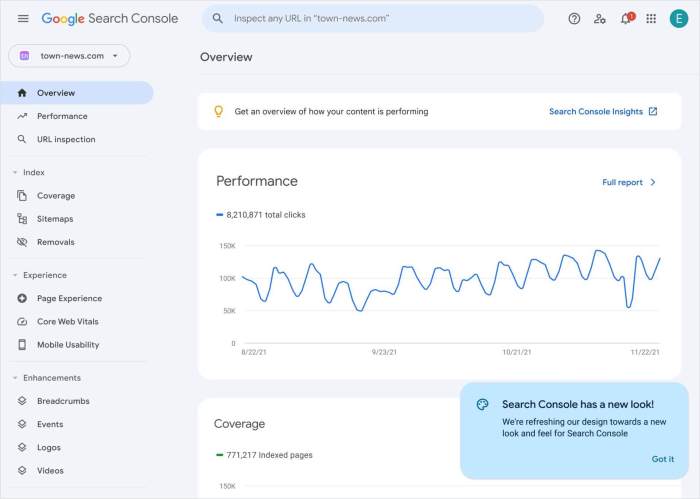
To get started with Google Search Console, follow these steps to set up your account and verify ownership of your website.
Creating a Google Search Console Account
- Go to the Google Search Console website and sign in with your Google account.
- Click on the “Add Property” button and enter your website URL.
- Choose a verification method to prove ownership of the website.
Verification Process for Different Websites
- HTML File Upload: Download the HTML file provided by Google and upload it to your website’s root directory.
- HTML Tag: Add the HTML tag provided by Google to the section of your website’s homepage.
- DNS Record: Create a new DNS TXT record with the verification code provided by Google.
- Google Analytics: If you have Google Analytics set up for your website, you can verify ownership through that account.
Verifying ownership is crucial as it allows you to access important data about your website’s performance and presence in Google search results.
Using Performance Reports: Using Google Search Console
When it comes to maximizing your website’s visibility and click-through rates, the performance reports section in Google Search Console is your go-to tool. This feature provides valuable insights into how your site is performing in search results and helps you identify areas for improvement.
Navigating the Performance Reports Section
- Access the performance reports section by logging into your Google Search Console account and selecting the property you want to analyze.
- Once you’re in the performance reports dashboard, you can customize the date range, filter by specific queries, pages, countries, and devices to get detailed insights.
- Explore the different tabs such as Total Clicks, Total Impressions, Average CTR, and Average Position to understand how your website is performing.
Key Metrics to Track
- Clicks: The number of times users clicked on your website in search results.
- Impressions: The number of times your website appeared in search results.
- CTR (Click-Through Rate): The percentage of users who clicked on your website after seeing it in search results.
- Average Position: The average ranking position of your website in search results.
Analyzing Data for Improvement
- Identify high-performing queries and pages with a high CTR but low average position to optimize them for better visibility.
- Focus on improving meta titles, descriptions, and content for pages with low CTR to increase user engagement.
- Monitor changes in performance over time to track the impact of strategies and content updates on your website’s visibility.
Index Coverage and Sitemaps
When it comes to optimizing your website for search engines, understanding index coverage and utilizing sitemaps are crucial aspects. Index coverage in Google Search Console provides insights into which pages of your site have been indexed by Google and which ones may have issues preventing them from being crawled or indexed.
Significance of Index Coverage
- Index coverage helps you identify pages that are not being indexed by Google, allowing you to take corrective actions to improve visibility.
- It also highlights any errors or warnings that may be affecting the indexing of your site, such as crawl errors, noindex tags, or server issues.
- By monitoring index coverage regularly, you can ensure that your most important pages are being indexed and are visible in search results.
Role of Sitemaps
- Sitemaps act as a blueprint of your website, helping search engines like Google understand the structure and organization of your content.
- Submitting a sitemap to Google Search Console can expedite the indexing process, especially for new or updated content on your site.
- Managing sitemaps effectively involves regularly updating them with new URLs, removing outdated ones, and resolving any errors that may arise.
Common Issues and Troubleshooting
- If you notice a large number of pages with errors in index coverage, check for issues such as duplicate content, broken links, or manual actions from Google.
- Ensure that your sitemap is correctly formatted and does not contain any errors that could prevent Google from properly crawling and indexing your site.
- If certain pages are not being indexed, check for issues like noindex tags, canonicalization problems, or crawlability issues that may be blocking Google’s access to those pages.